
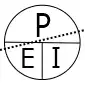
Ohm’s Law
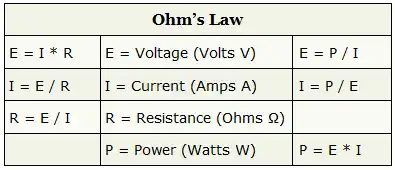
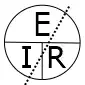
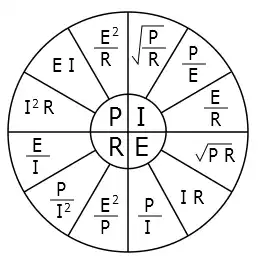
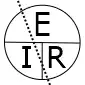
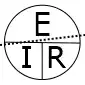
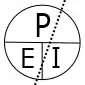
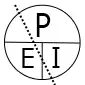
Voltage, current, resistance, and power can be calculated using ohm’s law. Below are the formulas for these calculations. At a given voltage when resistance increases, current decreases. When resistance decreases, current increases. The chart below left shows the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. The chart below right shows the relationship between power, voltage, and current.
Ohm’s Law Calculations
Expanded Ohm’s Law Chart
12 Volt 60 Watt Light Bulb Circuit
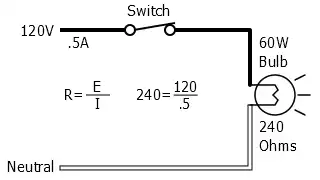
120 Volt 60 Watt Light Bulb Circuit
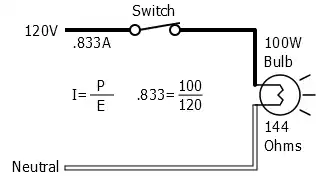
120 Volt 100 Watt Light Bulb Circuit
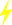
Voltage (E) and power (W) are known, how to calculate current (I).
Voltage (E) and power (W) are known, how to calculate current (I).
Voltage (E) and current (I) are known, how to calculate resistance (R).